I don’t know if you have such an experience: when you go shopping, a beauty consultant with exquisite makeup and body will walk towards you. She takes the initiative to chat up and starts doing some experience card marketing for you.
Each of these beauty consultants will:
Test your skin → Show you the need for skin care;
Ask about the skin care products you use → Speculate about your spending power;
Provide a project experience → Give you customized solutions, showing his professionalism;
Give you a good price → Highlight the high cost performance of beauty services.
Based on these 4 points and some psychological pressure, you may immediately like it /cannot refuse/try reluctantly and other reasons to buy the product.
If the in-person marketing is not successful, it doesn’t matter! Beauty salons have back-up tactics, such as:
Provide low price on holidays → Guide you into the store;
When you have a beauty treatment, there is always a consultant beside you → Guide you to buy a package card.
Become your WeChat friend, push “beauty will win” or “become a beauty girl” message to stimulate you every day→ Guide you to buy a package card.
The above several operations can always impress you once, so that you can happily buy the card and pay the fee.
Not only in the beauty salon, when you buy insurance/clothes/new house/hair card/ fitness card/membership card…This routine is widely used in marketing.
This is the famous MOT (Moment of Truth), which means “key moment”.
MOT (Moment of Truth):
Jan Carlson, former president of Scandinavian Airlines, describes the moment of truth (MOT) as the moment when a customer comes into contact with a company’s resources. This moment determines the success or failure of the business in the future, because for the customer, he will only remember those key moments (MOTs).
The significance of MOT theory for marketing is that if we can find (catch) the key moment of consumers in time, we are more likely to be able to influence them at the right time in the right way.
But in the digital age of information explosion, what consumers do throughout their life cycle journey is fragmented. For businesses, there is a huge amount of consumer data and a complex path of behavior every day, and consumers have a variety of touchpoints at different stages of their life cycle, across multiple devices (smartphones, tablets, PCS, etc.), platforms (mobile vs desktop web) and channels (paid, email, social, etc.). What kind of marketing action can motivate consumers to finally complete the conversion? What kind of consumer background and behavior path is behind this transformation?
With the development of big data technology, Social Hub tracks and analyzes the consumer journey through CDP and forms a variety of attribution analysis models to help businesses seize the marketing MOT.
1) Single platform channel attribution
Taking Social Hub CDP as an example, after the SDK integration of the client, the SDK will record the document.referrer of the user when he comes to the current page, then parse the url, and mark it on the user (first source channel, first utm source, etc.). The subsequent user behavior will be recorded through the track method; Based on this, we can make a single channel attribution to the user.
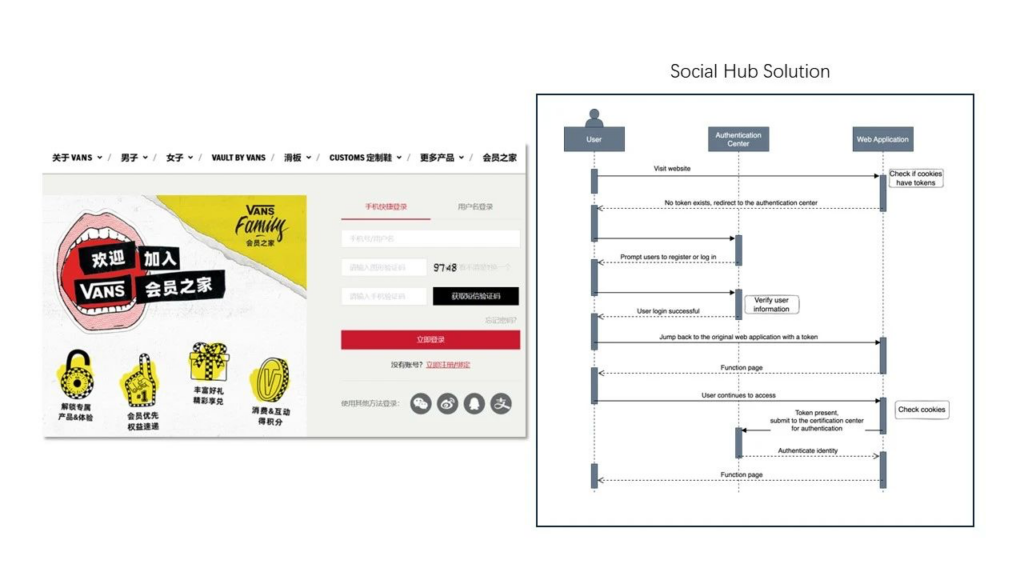
2) Cross-channel user attribution
Cross-channel attribution is so complex that it seems to be “unmeasurable.”
In the process of cross-channel attribution analysis, Social Hub CDP serves as a platform to help enterprises track end-to-end customer data. It can help marketing departments to obtain basic data efficiently and display reports in a visual way, lowering the threshold of data preparation and tools, and enabling business personnel to focus on the formulation and optimization of attribution strategies.
First of all, it is necessary to unify the user’s id across channels to form a large 360-degree view of the user, which will contain where the user comes from (channel information), his basic information (identity attributes) and behavior information (behavior records); Taking the Social Hub CDP as an example, when a user enters the product anonymously, the Social Hub CDP records the user’s behavior information and basic device information, and generates an id (the unique id within the Social Hub) (that is, the one id policy). After the user’s real name, if you can use the identify method (id mapping), the system associates the information before and after the user’s real name, such as the user’s name and mobile phone number. Then in the user profile, you can clearly know the source information of each platform before and after the user’s real name.
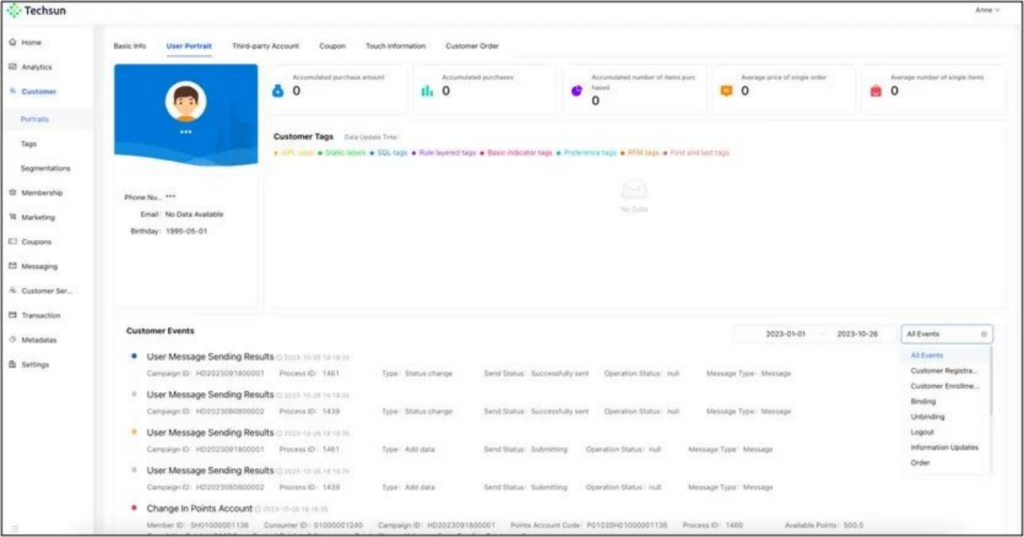
3) Behavior attribution
In most businesses are concerned about the key conversion behaviors of consumers, the business team often needs to know what factors lead to the ultimate conversion, and then optimize the enterprise’s own marketing link or strategy. Therefore, we need to trace the key behaviors of consumers, and we generally call this type of scenario behavioral attribution.
How to make behavioral attribution?
Funnel: For forward behavioral attribution of key transforming behaviors, funnel can be used to find out which values contribute the most to the transformation by using the ability to transform and subdivide steps between behaviors.
Path: Through path analysis, we can well discover the flow characteristics of users, find out from which links, which pages are lost, or obstacles, so as to optimize marketing strategies and improve performance.
Event: In the retail scenario, the key transformation behavior is payment. If we want to make attribution analysis on the payment behavior, we can analyze the “payment success” event through the event module in the Social Hub CDP and subdivide the event according to the primary source channel, then we can see the contribution ability of each channel, which is also a way of attribution.
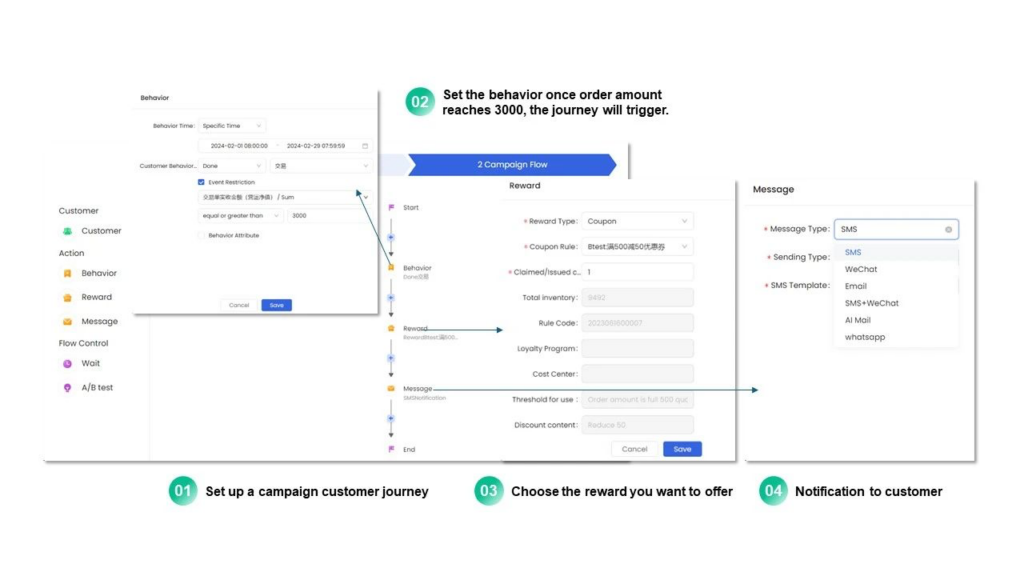
4) Other attribution models
There are many types of attribution models. In addition to the common business scenario attribution models listed above, some in-depth attribution models are also needed in very few business scenarios, such as first contact attribution, last contact attribution, linear attribution, potential customer conversion contact attribution, time decay attribution, location-based attribution, customized attribution model, etc. These models tend to be more complex and generally require professional data analysts to set up, which will not be expanded here.
While no attribution model can provide perfect data, a good attribution analysis process can definitely help companies get a direction. Social Hub’s CDP is able to bridge the gap between decentralized data and actionable analytics, establishing an automated attribution analysis process.
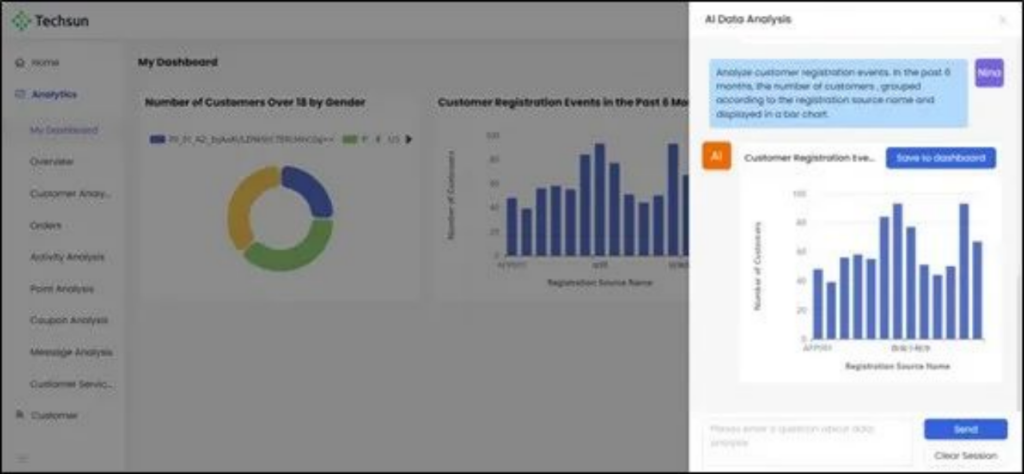
With the introduction of AIGC technology, the CDP of Social Hub has been upgraded by leaps and bounds in both art and science. In the background, AIGC uses deep learning algorithms to achieve high accuracy in data analysis, automatically generate reports containing key business indicators, intelligently group customers, and autonomously generate marketing strategies based on market trends and consumer behavior. On the front end, it can also provide customer service conversations full of language art and personalized recommendations based on consumer MOTs.
The future of marketing belongs to brands that are able to see changes in the market, keep up with consumer needs, and constantly innovate marketing strategies. Social Hub uses data-driven marketing to help brands take the lead in the digital age and achieve in-depth MOT interactive marketing with consumers. Click here to learn how AI Marketing Cloud can help you.
Source: Techsun Inc (Social Hub.AI)
10 Things You Need to Know About Smart Farming

With the global population expected to reach a staggering 9.7 billion by 2050, the demand for food production has never been more critical. To ensure that this growing population is…

